2025/6/22大约 10 分钟约 3129 字
通俗易懂解读BPE分词算法实现
BPE (Byte Pair Encoding)
BPE(Byte Pair Encoding,字节对编码)是一种基于频率统计的子词分词算法 ,广泛用于现代自然语言处理任务中,特别是在像 BERT、GPT 和 LLaMA 这样的大模型中。它的核心思想是通过不断合并最常见的字符对来构建一个高效的词汇表。
BPE 的核心思想:
从字符级别开始,逐步合并高频的字符对。
最终生成一个既能表示常见单词,又能拆解未知词的子词词汇表 。
可以有效控制词汇表大小,同时避免“未登录词”问题(OOV, Out-of-Vocabulary)。
预训练过程
BPE 算法预训练工作流程:
训练语料为: Hello World , Hey Wow
1. 读取训练语料,同时完成断句分词任务
# filepaths: 训练语料所在的文件列表
def create_vocab(filepaths: List[str]) -> Dict[str, int]:
# 获取所有单词和每个单词的出现次数词典
vocab = defaultdict(int)
for path in tqdm(filepaths, desc='Creating vocabulary'):
text = open(path, 'r', encoding='utf-8-sig').read()
# 利用NLTK库提供的sent_tokenize方法完成断句功能,即将原文本按照空格,句号等标点符号结合语义进行断句。
sentences = sent_tokenize(text)
# 遍历句子列表
for sentence in sentences:
# 利用NLTK库提供的wordpunct_tokenize方法完成分词功能
tokens = wordpunct_tokenize(sentence)
# 记录每个词的出现次数
for token in tokens:
vocab[token] += 1
# vocab: 记录每个词的出现次数的词典
return vocab
2. 过滤掉vocab中的低频词
def truncate_vocab(vocab: Dict[str, int], mincount: int) -> None:
tokens = list(vocab.keys())
for token in tokens:
if vocab[token] < mincount:
del(vocab[token])示例中设置为了1,不会过滤掉任何词。
3. 数据预处理
- 将训练语料中的每个单词按字符拆分,并在结尾加上特殊标记
</w>表示单词结束。
def prepare_bpe_vocab(vocab: Dict[str, int]) -> Dict[str, int]:
bpe_vocab = {}
# 遍历vocab中所有词
for token in vocab:
# 每个词的每个字符后都加上空格,同时末尾加上 </w> 表示单词结束
ntoken = ' '.join(list(token)) + ' </w>'
bpe_vocab[ntoken] = vocab[token]
return bpe_vocab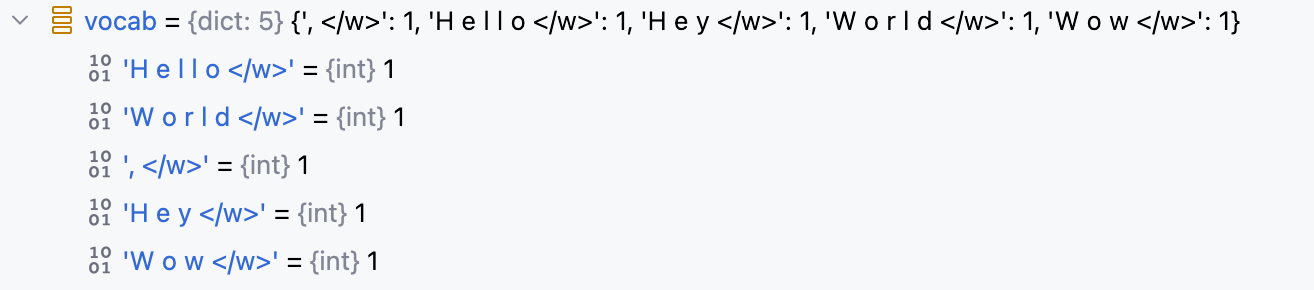
4. 经历N次迭代,合并前N个最频繁的字符对
# 一共合并merges个高频字符对后,才结束词汇表的构建
for i in trange(merges, desc='Merging'):
# 1. 获取每个相邻字符对的出现次数
pairs = get_stats(vocab)
# 2. 获取当前最高频的字符对
best = max(pairs, key=pairs.get)
# 3. 合并当前最高频的字符对
vocab = merge_vocab(best, vocab)
######记录历史合并的最高频子词对及其频率(传统BPE算法没有这一步)######
merged_pair_freqs = defaultdict(int)
# 一共合并merges个高频字符对后,才结束词汇表的构建
for _ in trange(merges, desc='Merging'):
# 1. 获取每个相邻字符对的出现次数
pairs = get_stats(vocab)
# 2. 获取当前最高频的字符对
best_pair = max(pairs.items(), key=lambda x: x[1])
######记录该子词对的全局频率(传统BPE算法没有这一步)######
best_subword = ''.join(best_pair[0])
best_freq = best_pair[1]
merged_pair_freqs[best_subword] += best_freq
# 3. 合并当前最高频的字符对
vocab = merge_vocab(best_pair[0], vocab)4.1 获取每个相邻字符对的出现次数
def get_stats(vocab: Dict[str, int]) -> Dict[Tuple[str, str], int]:
pairs = defaultdict(int)
for word, freq in vocab.items():
# 对经过预处理的vocab中的每个词按空格进行切分
symbols = word.split()
# 统计每个相邻字符对的出现次数
for i in range(len(symbols)-1):
pairs[symbols[i],symbols[i+1]] += freq
return pairs
4.2 获取当前最高频的字符对

4.3 合并当前最高频的字符对
def merge_vocab(pair: Tuple[str, str], v_in: Dict[str, int]) -> Dict[str, int]:
# 1. 将传入的最高频字符对中的两个字符用空格拼接起来,如: "H e"
bigram = re.escape(' '.join(pair))
v_out = {}
# 2. 正则匹配含有“H e”的所有单词,并且“H”和“e”必须为两个独立的词,而不能为"HH e"或者"H ee"形式
p = re.compile(r'(?<!\S)' + bigram + r'(?!\S)')
# 3. 遍历vocab中所有词
for word in v_in:
# 3.1 用正则匹配并替换匹配上的 "H e" 为 “He”
w_out = p.sub(''.join(pair), word)
v_out[w_out] = v_in[word]
# 4. 返回合并最高频字符对后的vocab
return v_out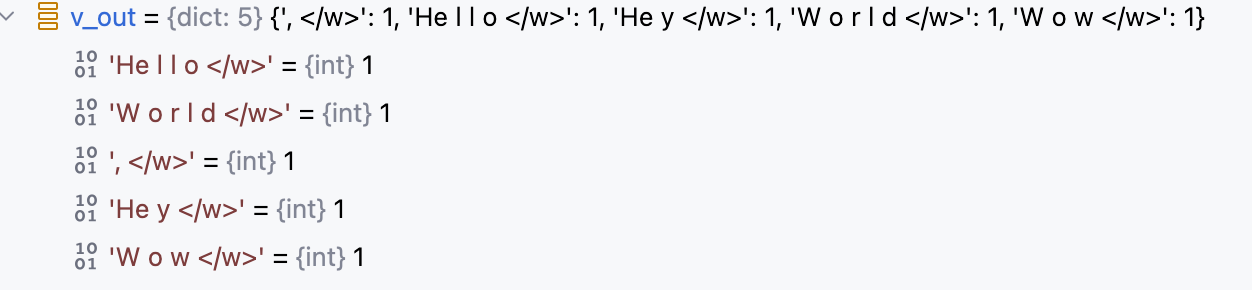
5.根据N轮迭代合并后的Vocab来构建最终的频次表(每个子词的出现次数)
def count_byte_freqs(vocab: Dict[str, int]) -> Dict[str, int]:
freqs = defaultdict(int)
for word in vocab:
# 1. 按空格切分
bytes_ = word.split(' ')
# 2. 每个子词出现次数加1
for byte in bytes_:
freqs[byte] += 1
# 3. 添加一些特殊词
for token in ['<line/>', '</line>', '<pad>', '<unk>']:
freqs[token] += 1
return freqs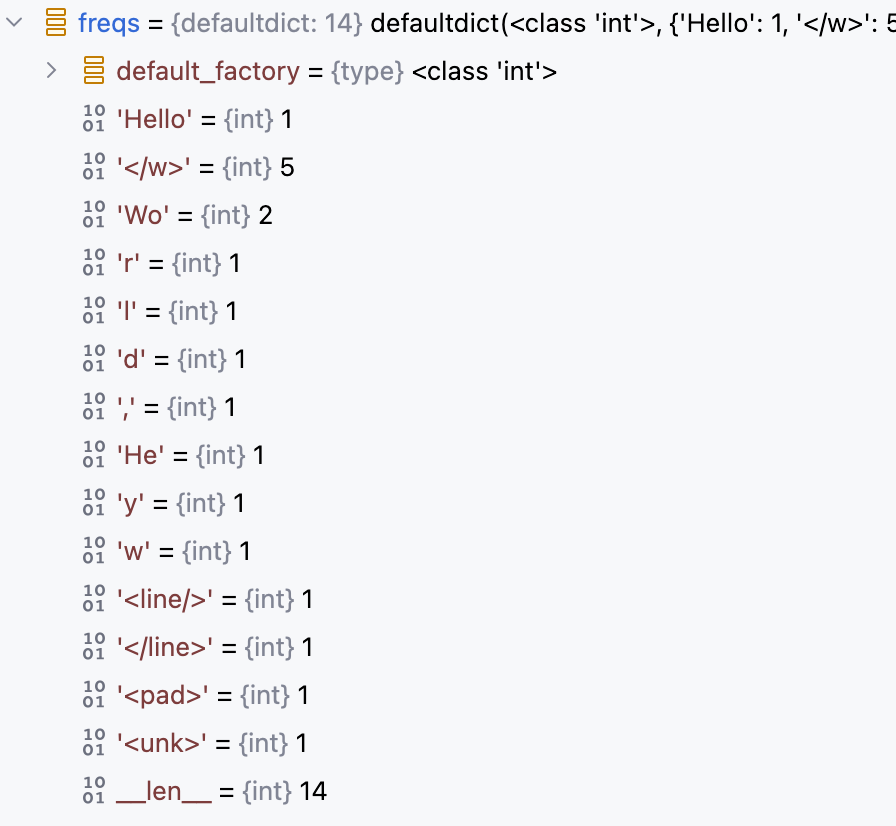
6.根据频次表构建最终的词汇表
def create_vocab_maps(freqs: Dict[str, int]) -> (Dict[str, int], Dict[int, str]):
# 1. 按照 词频从高到低 的顺序排序
ordered_freqs = sorted(freqs.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
vocab_to_idx, idx_to_vocab = {}, {}
for i in range(len(ordered_freqs)):
# 2. 构建词汇表
word, freq = ordered_freqs[i]
vocab_to_idx[word] = i
idx_to_vocab[i] = word
return vocab_to_idx, idx_to_vocab
7. freqs = 最终子词频率 + 历史最高频合并对的频率(传统BPE算法没有这一步)
freqs.update(merged_pair_freqs)
8. 通常最后会将预训练生成的频次表和词汇表写入文件保存
def save(self, path: str) -> None:
# 1. 频次表记录合并规则,也就是有哪些子词以及这些子词的出现次数,作为分词时的合并规则和优先选择权
with open(f'{path}/freqs.json', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as outfile:
json.dump(self.freqs, outfile, indent=4, ensure_ascii=False)
# 2. 常规的词汇表
with open(f'{path}/vocab_to_idx.json', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as outfile:
json.dump(self.vocab_to_idx, outfile, indent=4, ensure_ascii=False)
with open(f'{path}/idx_to_vocab.json', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as outfile:
json.dump(self.idx_to_vocab, outfile, indent=4, ensure_ascii=False)BPE 算法预训练过程完整代码如下
def train_bpe(filepaths: List[str], mincount: int, merges: int) -> 'BytePairTokenizer':
vocab = create_vocab(filepaths)
truncate_vocab(vocab, mincount)
vocab = prepare_bpe_vocab(vocab)
merged_pair_freqs = defaultdict(int) # (传统BPE算法没有这一步)
for _ in trange(merges, desc='Merging'):
pairs = get_stats(vocab)
best_pair = max(pairs.items(), key=lambda x: x[1])
best_subword = ''.join(best_pair[0]) # (传统BPE算法没有这一步)
best_freq = best_pair[1] # (传统BPE算法没有这一步)
merged_pair_freqs[best_subword] += best_freq # (传统BPE算法没有这一步)
vocab = merge_vocab(best_pair[0], vocab)
freqs = count_byte_freqs(vocab)
vocab_to_idx, idx_to_vocab = create_vocab_maps(freqs)
freqs.update(merged_pair_freqs) # (传统BPE算法没有这一步)
return BytePairTokenizer(freqs, vocab_to_idx, idx_to_vocab)分词过程
1.对输入的文本进行断句加分词
# 使用NLTK库提供的sent_tokenize方法进行分词
lines = sent_tokenize(open(filepath, encoding='utf-8-sig').read())
tokens = []
# 遍历所有句子
for line in lines:
if len(line) > 1:
tokens += get_line_ids(line, tokenizer)def get_line_ids(line: str, tokenizer: BytePairTokenizer) -> List[int]:
# 对每个句子进行分词
tokens = wordpunct_tokenize(line)
# 将每个词从str转换为list列表形式,同时列表末尾追加</w>
tokens = [list(t) + ['</w>'] for t in tokens]
...以输入 "Hello World" 为例
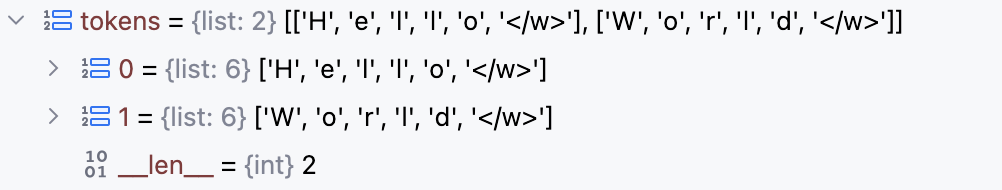
2. 对当前句子中每个词进行子词合并加词ID映射,最后得到当前句子对应的Token列表
def get_line_ids(line: str, tokenizer: BytePairTokenizer) -> List[int]:
...
lineids = []
for token in tokens:
# 2.1 对每个词进行子词合并,直到无法合并为止
token = tokenizer.merge_bytes(token)
# 2.2 将当前词列表中每个子词映射为字典中对于的词ID
ids = tokenizer.get_byte_ids(token)
lineids += ids
sol_id = tokenizer.get_byte_id('<line/>')
eol_id = tokenizer.get_byte_id('</line>')
lineids = [sol_id] + lineids + [eol_id]
return lineids2.1 对每个词进行子词合并,直到无法合并为止
# 对当前词的子词进行合并,直到无法合并为止
def merge_bytes(self, bytes_: List[str]) -> List[str]:
bytes_, merged = self.merge_max_pair(bytes_)
while merged:
bytes_, merged = self.merge_max_pair(bytes_)
return bytes_
def merge_max_pair(self, bytes_: List[str]) -> (List[str], bool):
# 1. 取出出现次数最多的字符对
max_pair = self.get_max_pair_idxs(bytes_)
merged = True if max_pair is not None else False
if merged:
# 2. 合并该字符对
bytes_ = bytes_[:max_pair[0]] + \
[''.join(bytes_[max_pair[0]:max_pair[1]+1])] + \
bytes_[max_pair[1]+1:]
return bytes_, merged
def get_max_pair_idxs(self, bytes_) -> Tuple[int, int]:
pairs = {}
# 1. 遍历所有相邻字符对的组合
for i in range(1, len(bytes_)):
pair = ''.join(bytes_[i-1:i+1])
# 2. 判断每个字符对是否存在于频次表中,如果存在记录出现次数
if pair in self.freqs:
pairs[(i-1, i)] = self.freqs[pair]
# 3. 取出出现次数最多的字符对
return None if len(pairs) == 0 else max(pairs, key=pairs.get)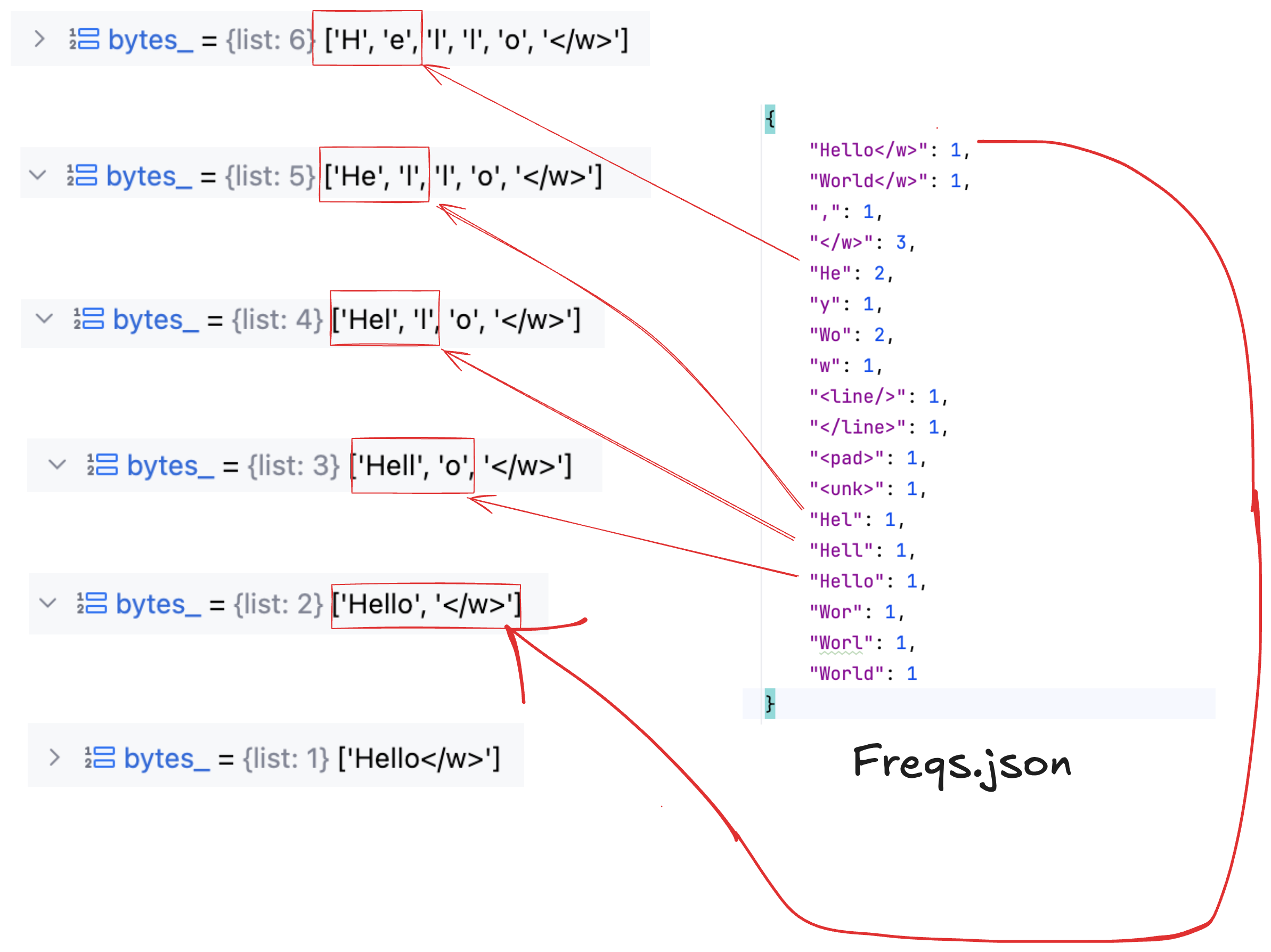
2.2 将当前词列表中每个子词映射为字典中对于的词ID
def get_byte_ids(self, bytes_):
ids = []
for byte in bytes_:
if byte in self.vocab_to_idx:
ids.append(self.vocab_to_idx[byte])
else:
ids.append(self.vocab_to_idx[self.unk])
return ids附录
BPE 分词器完整代码实现:
from typing import Tuple, Dict, List
from collections import defaultdict
import json, re
from nltk import wordpunct_tokenize, sent_tokenize
from tqdm import trange, tqdm
class BytePairTokenizer:
def __init__(self, freqs: Dict[str, int], vocab_to_idx: Dict[str, int],
idx_to_vocab: Dict[int, str]):
""" Initialize byte pair tokenizer
Args:
freqs: frequency dictionary of vocabulary
vocab_to_index: map of vocabulary words to indices
index_to_vocab: map of vocabulary indices to words
"""
self.vocab_to_idx = vocab_to_idx
self.idx_to_vocab = idx_to_vocab
self.freqs = freqs
self.sol = '<line/>'
self.eol = '</line>'
self.pad = '<pad>'
self.unk = '<unk>'
self.eow = '</w>'
def get_sol(self) -> str:
return self.sol
def get_eol(self) -> str:
return self.eol
def get_pad(self) -> str:
return self.pad
def get_unk(self) -> str:
return self.unk
def get_eow(self) -> str:
return self.eow
def get_byte(self, byte_id: int) -> str:
return self.idx_to_vocab[byte_id]
def get_byte_id(self, byte: str) -> int:
unk_id = self.vocab_to_idx[self.unk]
bid = self.vocab_to_idx[byte] if byte in self.vocab_to_idx else unk_id
return bid
def get_byte_ids(self, bytes_):
""" Get byte ids for each byte in provided list
"""
ids = []
for byte in bytes_:
if byte in self.vocab_to_idx:
ids.append(self.vocab_to_idx[byte])
else:
ids.append(self.vocab_to_idx[self.unk])
return ids
def get_bytes(self, byte_ids: List[int]) -> List[str]:
""" Given a list of byte ids return corresponding bytes
Args:
byte_ids: list of byte ids
Returns:
(List[str]): list of bytes
"""
tokens = []
for byte_id in byte_ids:
tokens.append(self.idx_to_vocab[byte_id])
return tokens
def merge_bytes(self, bytes_: List[str]) -> List[str]:
""" Return list of bytes with max pair merged
Args:
bytes_: list to merge max pair in
Returns:
(List[str]): list of bytes with all max pair occurrences merged
"""
bytes_, merged = self.merge_max_pair(bytes_)
while merged:
bytes_, merged = self.merge_max_pair(bytes_)
return bytes_
def merge_max_pair(self, bytes_: List[str]) -> (List[str], bool):
""" Takes in a list of bytes and merges the max pair if possible
Args:
bytes_: list of bytes to merge max pair in
Returns:
(bytes_): list of bytes with max pair merged
(bool): flag indicating whether merge occurred
"""
max_pair = self.get_max_pair_idxs(bytes_)
merged = True if max_pair is not None else False
if merged:
bytes_ = bytes_[:max_pair[0]] + \
[''.join(bytes_[max_pair[0]:max_pair[1]+1])] + \
bytes_[max_pair[1]+1:]
return bytes_, merged
def get_max_pair_idxs(self, bytes_) -> Tuple[int, int]:
""" Get index of maximum byte pair in list of bytes
Args:
bytes_: list of bytes to find maximum pair from
Returns:
(Tuple[int, int]): maximum frequency byte pair
"""
pairs = {}
for i in range(1, len(bytes_)):
pair = ''.join(bytes_[i-1:i+1])
if pair in self.freqs:
pairs[(i-1, i)] = self.freqs[pair]
return None if len(pairs) == 0 else max(pairs, key=pairs.get)
def save(self, path: str) -> None:
with open(f'{path}/freqs.json', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as outfile:
json.dump(self.freqs, outfile, indent=4, ensure_ascii=False)
with open(f'{path}/vocab_to_idx.json', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as outfile:
json.dump(self.vocab_to_idx, outfile, indent=4, ensure_ascii=False)
with open(f'{path}/idx_to_vocab.json', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as outfile:
json.dump(self.idx_to_vocab, outfile, indent=4, ensure_ascii=False)
@staticmethod
def load(path: str) -> 'BytePairTokenizer':
with open(f'{path}/freqs.json', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as infile:
freqs = json.load(infile)
with open(f'{path}/vocab_to_idx.json', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as infile:
vocab_to_idx = json.load(infile)
with open(f'{path}/idx_to_vocab.json', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as infile:
idx_to_vocab = json.load(infile)
return BytePairTokenizer(freqs, vocab_to_idx, idx_to_vocab)
@staticmethod
def train_bpe(filepaths: List[str], mincount: int, merges: int) -> 'BytePairTokenizer':
vocab = create_vocab(filepaths)
truncate_vocab(vocab, mincount)
vocab = prepare_bpe_vocab(vocab)
merged_pair_freqs = defaultdict(int)
for _ in trange(merges, desc='Merging'):
pairs = get_stats(vocab)
if not pairs:
break
best_pair = max(pairs.items(), key=lambda x: x[1])
best_subword = ''.join(best_pair[0])
best_freq = best_pair[1]
merged_pair_freqs[best_subword] += best_freq
vocab = merge_vocab(best_pair[0], vocab)
freqs = count_byte_freqs(vocab)
vocab_to_idx, idx_to_vocab = create_vocab_maps(freqs)
freqs.update(merged_pair_freqs)
return BytePairTokenizer(freqs, vocab_to_idx, idx_to_vocab)
def create_vocab(filepaths: List[str]) -> Dict[str, int]:
""" Create dictionary of vocabulary frequencies in given list of files
Args:
filepaths: list of filepaths to collect vocabulary from
Returns:
(Dict[str, int]): dictionary mapping vocabulary terms to their frequency
"""
vocab = defaultdict(int)
for path in tqdm(filepaths, desc='Creating vocabulary'):
text = open(path, 'r', encoding='utf-8-sig').read()
sentences = sent_tokenize(text)
for sentence in sentences:
tokens = wordpunct_tokenize(sentence)
for token in tokens:
vocab[token] += 1
return vocab
def truncate_vocab(vocab: Dict[str, int], mincount: int) -> None:
""" Truncate vocabulary dictionary based on a minimum count
Args:
vocab: frequency mapping dictionary to truncate
mincount: minimum count for members of dictionary (words with lower
frequencies will be removed)
"""
tokens = list(vocab.keys())
for token in tokens:
if vocab[token] < mincount:
del(vocab[token])
def prepare_bpe_vocab(vocab: Dict[str, int]) -> Dict[str, int]:
""" Prepare vocabulary frequency dictionary for byte-pair generation.
End-of-word byte '</w>' added to words, every character separated by space
Args:
vocab: vocabulary frequency dictionary to prepare
Returns:
(Dict[str, int]): byte-pair ready vocabulary frequency dictionary
"""
bpe_vocab = {}
for token in vocab:
ntoken = ' '.join(list(token)) + ' </w>'
bpe_vocab[ntoken] = vocab[token]
return bpe_vocab
def get_stats(vocab: Dict[str, int]) -> Dict[Tuple[str, str], int]:
""" Count all bytepairs in a dictionary containing vocabulary frequencies
Args:
vocab: dictionary mapping words to their frequency
Returns:
(Dict[Tuple[str, str], int]): dictionary containing byte pair
frequencies
"""
pairs = defaultdict(int)
for word, freq in vocab.items():
symbols = word.split()
for i in range(len(symbols)-1):
pairs[symbols[i],symbols[i+1]] += freq
return pairs
def merge_vocab(pair: Tuple[str, str], v_in: Dict[str, int]) -> Dict[str, int]:
""" Merge all instances of given byte pair in vocabulary frequency
dictionary
Args:
pair: byte pair to merge
v_in: vocabulary to merge byte pair int
Returns:
(Dict[str, int]): resulting vocabulary with all instances of given byte
pair merged
"""
bigram = re.escape(' '.join(pair))
v_out = {}
p = re.compile(r'(?<!\S)' + bigram + r'(?!\S)')
for word in v_in:
w_out = p.sub(''.join(pair), word)
v_out[w_out] = v_in[word]
return v_out
def count_byte_freqs(vocab: Dict[str, int]) -> Dict[str, int]:
freqs = defaultdict(int)
for word in vocab:
bytes_ = word.split(' ')
for byte in bytes_:
freqs[byte] += 1
for token in ['<line/>', '</line>', '<pad>', '<unk>']:
freqs[token] += 1
return freqs
def create_vocab_maps(freqs: Dict[str, int]) -> (Dict[str, int], Dict[int, str]):
""" Create map of vocabulary terms to indices and vice versa. Word indices
are in order of their frequency in the provided vocabulary
Args:
freqs: dictionary mapping vocabulary terms to their frequencies
Returns:
(Dict[str, int]): dictionary mapping vocab to indices
(Dict[int, str]): dictionary mapping indices to vocab
"""
ordered_freqs = sorted(freqs.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
vocab_to_idx, idx_to_vocab = {}, {}
for i in range(len(ordered_freqs)):
word, freq = ordered_freqs[i]
vocab_to_idx[word] = i
idx_to_vocab[i] = word
return vocab_to_idx, idx_to_vocab